Manually Configure a Gateway Server
This article covers adding a standalone, manually configured RD Gateway (as opposed to a Workspot Managed Gateway Cluster) to your Workspot datacenter. It is part of the Getting Started with Workspot article series.
Introduction
This document will walk through the process on how to manually configure a server as a secure Gateway and assumes that a Windows 2019 Server vm instance was already created and it has a static Public IP assigned to it. The Gateway server is typically deployed in a DMZ or Transit subnet.
Installing the Gateway Server Role
When creating a gateway from control is not an available option, the gateway can be manually configured.
To begin the process connecting the Gateway Instance using RDP from the Utility Server using the Gateway local administrator account.
Note: At the time of this documents creation manually installing and registering the Gateway Agent is not supported. Therefore, it will not send telemetry to Workspot Watch.
Once logged in, use the Server Manager…Local Server. If you want to rename the Gateway computer name do so now , check for updates, reboot, then log back in.
Use the ‘Server Manager’ go to ‘Local Server’ ‘Manage’ and select ‘Add Roles and Features’ and just click next on the wizard Introduction screen to begin the process.
On the Select Installation type page choose the default ‘Role-based or feature-based installation’
Click next to accept the default on the Server Selection page. On the Server role page put a checkmark next to the ‘Remote Desktop Services’ selection and click next. Accept the default on the ‘Select Features’ page and click next. Click next on the ‘Remote Desktop Services’ page. On the Role Services page choose ‘Remote Desktop Gateway’ and then accept the defaults for the ‘Add Features’ popup windows.
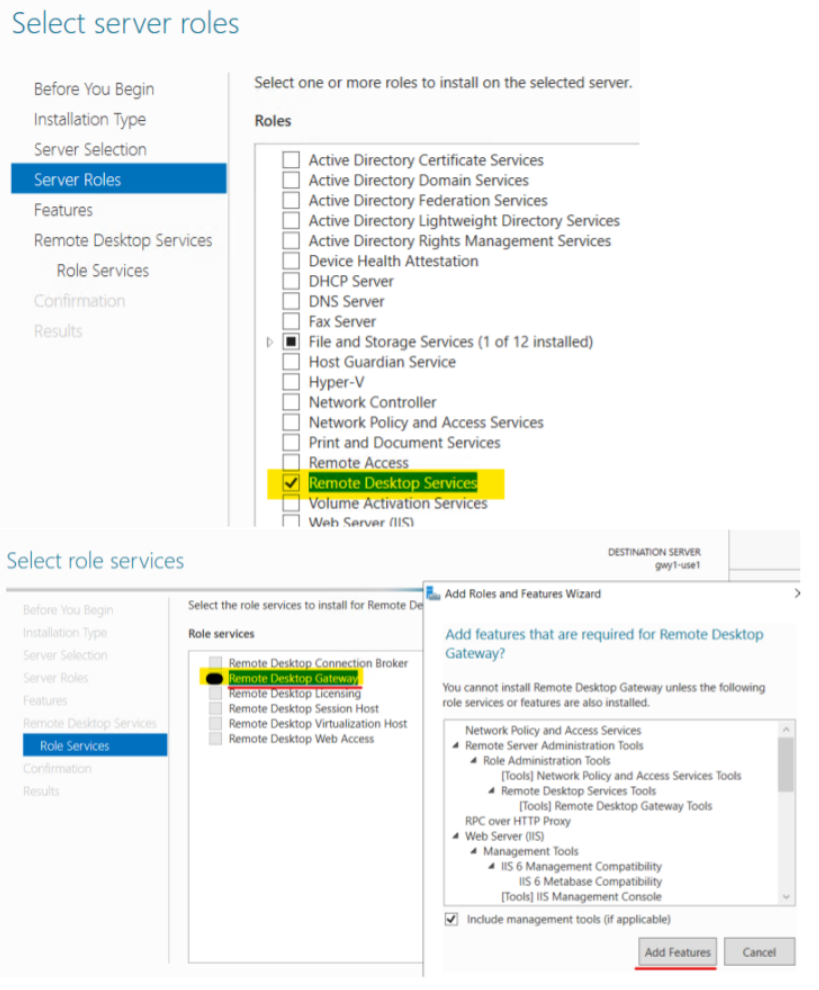
Just click next and accept the defaults on the remaining pages. Click ‘Install’ on the final page.
Join the Gateway Server to the Domain
Once the Role is installed use powershell to join the domain to the Workspot Servers OU
Example command:
Add-Computer -DomainName "wspoc.cloud" -OUPath "OU=Workspot Servers,DC=wspoc,DC=cloud"
Restart once the domain join is successful and log back in the local admin account. No requirement here to use a domain account.
Configure the Gateway
Once logged navigate to and launch the ‘RD Gateway Manager’ app. Select the Gateway Server to begin the configuration process. Only three (3) things need to be configured here. The Certificate, Connection Authorization and Resource Authorization policies.
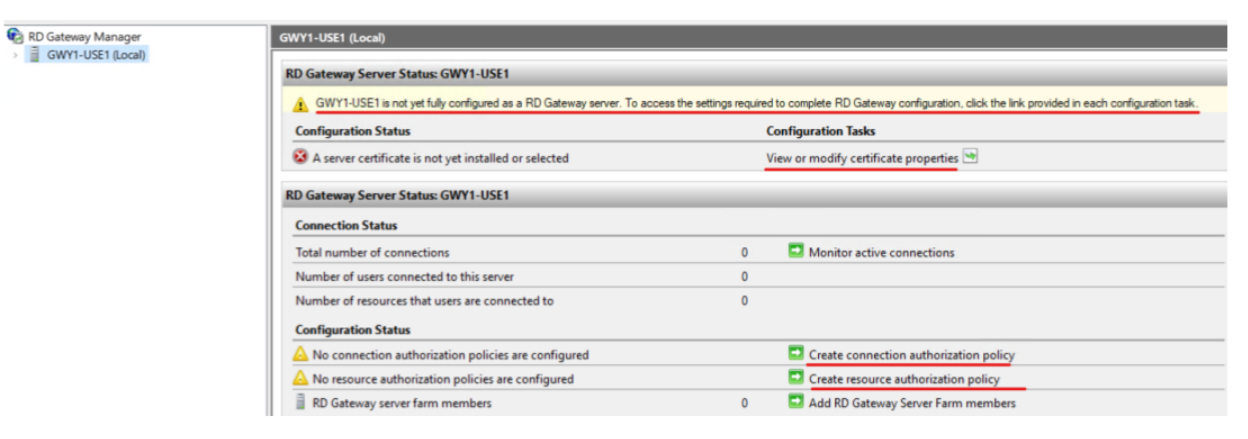
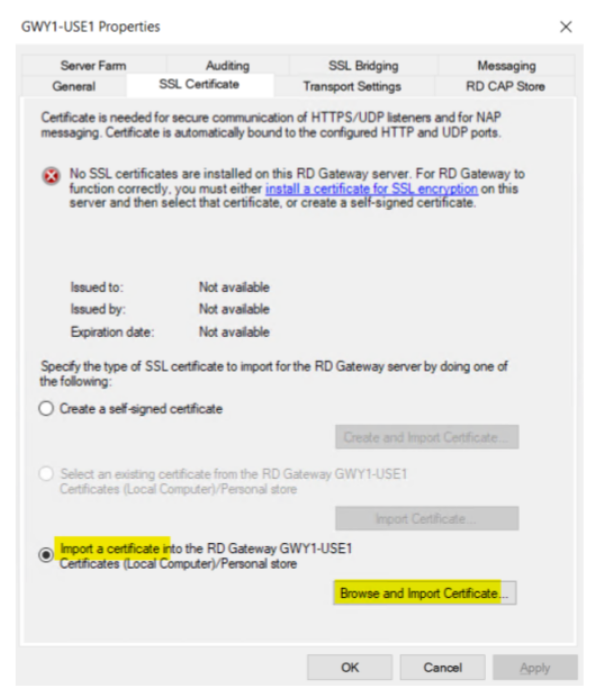
First Configuration Task is to click on the ‘View or modify certificate properties’ and then select the ‘Import a certificate’ radio button. Browse to the certificate, provide the Secret Key Password, and import the Certificate.
A public certificate and ability to register a domain name is the recommendation.
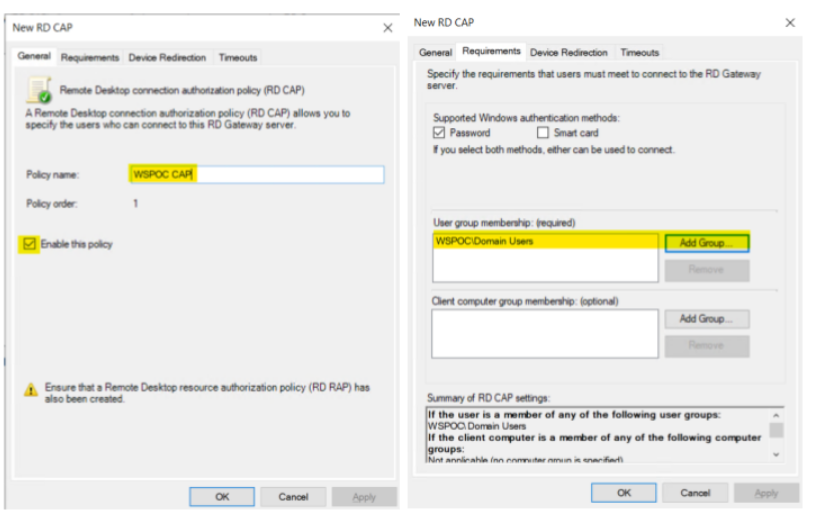
The next Configuration tasks are to create the ‘Connection Authorization policy’ (CAP) and ‘Resource Authorization Policy’ (RAP). For the sake of this exercise, we will configure the CAP and RAP as follows.
CAP – Only things to configure here for this exercise are on the ‘General’ and ‘Requirements’ tab, highlighted in the screenshot below. Accept the default on the other two (2) tabs.
RAP – Ensure the highlighted below is configured
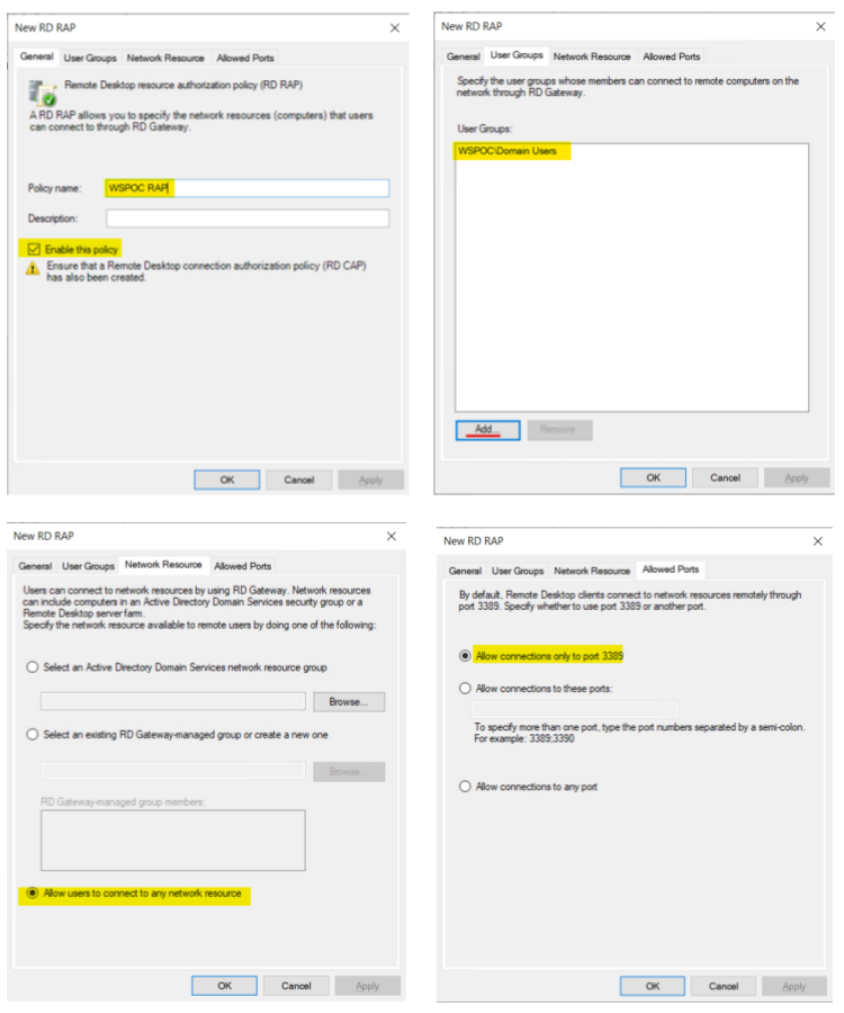
The Gateway role is now configured and ready when needed.
Register the Gateway DNS record
DNS ‘A’ record for the Gateway will be required.
You need to make sure the DNS ‘A’ record is configured with the domain name that is represented in your certificate and the Public IP that is associated with the Gateway Instance.
The only thing left to do is to add that gateway to Workspot control.
Add Gateway to Control
Logon to Control and navigate to ‘Setup…Gateways…Private Cloud Gateways’. Click on ‘Add Private Gateway’
Provide a friendly Gateway name and the Gateway URI (‘A’ record in public DNS)
For example:
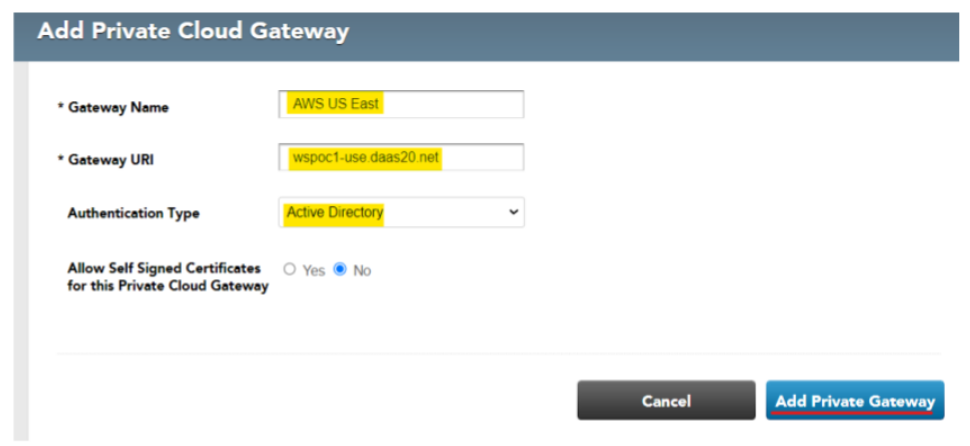
The Gateway is now linked to Control.


