Workspot Landing Zone
Last updated on April 18, 2024 by Robert Plamondon
This article covers the top-level network topology of your Workspot deployment and is part of the Getting Started with Workspot series.
The Workspot Landing Zone is the Cloud or on-premises network containing your Workspot desktop and app server pools. Think of it as the part of your network that you manage with Workspot Control. It is distinct from the rest of your organization’s network. If you place Landing Zones in multiple Clouds or regions, they are managed almost as easily as if they weren’t separate.
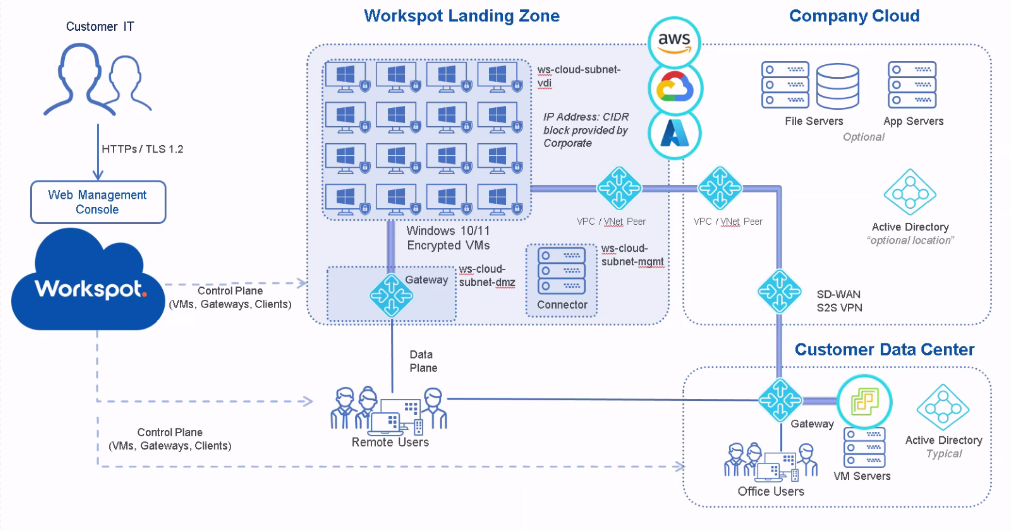
Landing Zone Diagram
Web Management Console (Workspot Cloud). This is the Workspot Control management portal and its associated services, including Workspot Watch and Workspot Trends. Workspot Control is where you create and manage desktop and app server pools, along with associated infrastructure like desktop templates and managed gateways. Management is the same for all Clouds.
Control Planes. Workspot Clients and the VMs in the Workspot Landing Zone open secure Internet connections to Workspot Control to report status and receive management commands. An additional path, not shown, contacts the Cloud provider’s API to create and manage VMs, perform power management, retrieve status information, and so on.
Data Plane. These are the end-user connections to their Workspot desktops and apps via the Workspot Managed Gateway.
Workspot Landing Zone. This is the landing zone proper, containing the Workspot desktop and app server VMs. In the diagram, it is divided into three subnets:
- Ws-cloud-subnet-vdi, containing the Workspot desktops,
- Ws-cloud-subnet-dmz, an isolated subnet containing only the Workspot managed gateways, and
- Ws-cloud-subnet-mgmt, an isolated subnet containing only the Workspot Connector.
- Gateway. End-user desktop/app sessions enter the landing zone through the Workspot Managed RD Gateway (labeled simply “Gateway” on the diagram). Entry from your corporate network passes through the VNET peer.
- Workspot Desktops. These are your end-user’s Windows or Linux desktop VMs inside the Landing Zone, created and managed in Workspot Control. Most aspects of desktop assignment and access are set by you via policies in Control. End-users access these desktops using a Workspot Client.
- VPC/VNET Peer. Connects the Workspot Landing Zone with your other Cloud resources.
- Connector. This is the Workspot Enterprise Connector, a service running on a Windows Server VM that makes read-only queries to your AD Domain Controller. Though shown in the Workspot Landing Zone, it is often deployed on the same LAN as your Domain Controller.
- IP Block. The Landing Zone should be routable within your organization’s private network.
Company Cloud. Your Cloud resources outside the Landing Zone but still relevant to your Workspot deployment:
- File Servers. These contain the file systems used by your Workspot desktops/apps (in addition to the boot drives that are part of the desktop/app server VMs themselves).
- App Servers. These are App Server VMs used by your Workspot desktops/apps.
- Active Directory. One possible location for a standalone or redundant AD Domain Controller. A Workspot Enterprise Controller should be deployed here as well.
- VPC/VNET Peer. The other side of the link to the Workspot Landing Zone.
- SD-WAN/S2S VPN. The link to your on-premises or other datacenters.
Remote Users. These are your end-users, who access their Workspot resources via the Workspot Client, available for Windows, Mac, Web browsers, iOS/iPadOS, and Android. Workspot resources and access to them is subject to restrictions in Workspot Control and those set up with your ID provider in addition to simple sign-in credentials. For example, users signing in over the Internet may require additional authentication, and different users are given access to different Workspot resources, such as a dedicated GPU workstation vs. a simple non-persistent desktop.
Customer Data Center. This example shows a data center with local Workspot users in addition to datacenter resources. Note that the “Gateway” block should be shown as two blocks: the second half of the SD-WAN/S2S VPN pair and a Workspot Managed RD Gateway, and the Active Directory Domain Controller should be paired with a Workspot Enterprise Connector.
Prerequisites
The following need to be selected, assigned, or performed before the Workspot Landing Zone can be created:
- Supported Public Cloud (Azure, GCP, AWS) or Private Cloud (vSphere, Nutanix)
- Administrator permissions to Cloud
- A network CIDR block for Virtual Network configuration.
- Review Workspot Network Port Requirements and Security.
- A supported Identity Provider (such as Microsoft Active Directory, Microsoft Azure Active Directory, OKTA, etc.)
- Connectivity to Microsoft Active Directory or Domain Controller on the virtual network
- A supported operating system for VDI desktops, RD Pools servers and Workspot infrastructure components: Workspot OS and Hardware Requirements.
- Optional network connectivity to on-premises such as Site-to-Site VPN
AWS Workspaces Core
- AWS Account with BYOL and BYOP enabled. See Amazon’s article on BYOL Windows Images.
- AWS Directory Services - AD Connector configured. See Amazon’s AD Connector article.
- AWS Workspaces enabled and configured.
- Ensure Enable Dedicated Workspaces during Directory registration. See Amazon’s Dedicated directory for Workspaces.
AWS EC2
- Dedicated Host to support BYOL desktops.
- Enabled AWS License Manager for Dedicated Host. See Amazon’s dedicated host article.
GCP
- Sole-tenant nodes to support BYOL desktops.
- Shared VPC is not supported currently.
Azure
- Ensure necessary Resource Providers are registered such as Microsoft.Compute, Microsoft.Storage and Microsoft.Network. See Microsoft’s Resource Management article.
All Public Clouds
For any of the Clouds above:
- Create a Public Cloud (Azure subscription, GCP Project or AWS Account) that is dedicated to Workspot.
- Leave everything in the Public Cloud at the defaults.
- The Public Cloud will require Public IPs for the Workspot Managed Gateways.
Private Cloud (On-Premises)
The following environments are supported:
- VMware ESX/ESXi 7.0 or later.
- vCenter Server Appliance 7.0 or later.
- Nutanix
Also required:
- DHCP enabled network providing IPs for VDI desktops
Networking
Create a Virtual Network i.e. ws-cloud-vpc with three subnets:
- Gateway Subnet - subnet used to provision or create Workspot managed gateways on, i.e. ws-cloud-subnet-dmz
- Management Subnet - subnet used to create Workspot Enterprise Connector on, i.e. ws-cloud-subnet-mgmt
- Cloud VDI Subnet - subnet used to provision Workspot VDI desktops on, i.e ws-cloud-subnet-vdi
- Assign a CIDR block. For example: 10.0.0.0/20
- The CIDR block cannot overlap with any other CIDR block within the private network when connecting this GCP project to the private network.
- Provide a large enough block of IP addresses to allow for expansion over time.


